Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
Are you an architecture fan?
Some of these terms describe popular styles of architecture.
Others describe specific terms that you may recognize but did not know what the design element was called.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
Keep reading to see how many terms you recognize!
Here are over 100 architecture terms that will help you describe buildings better!
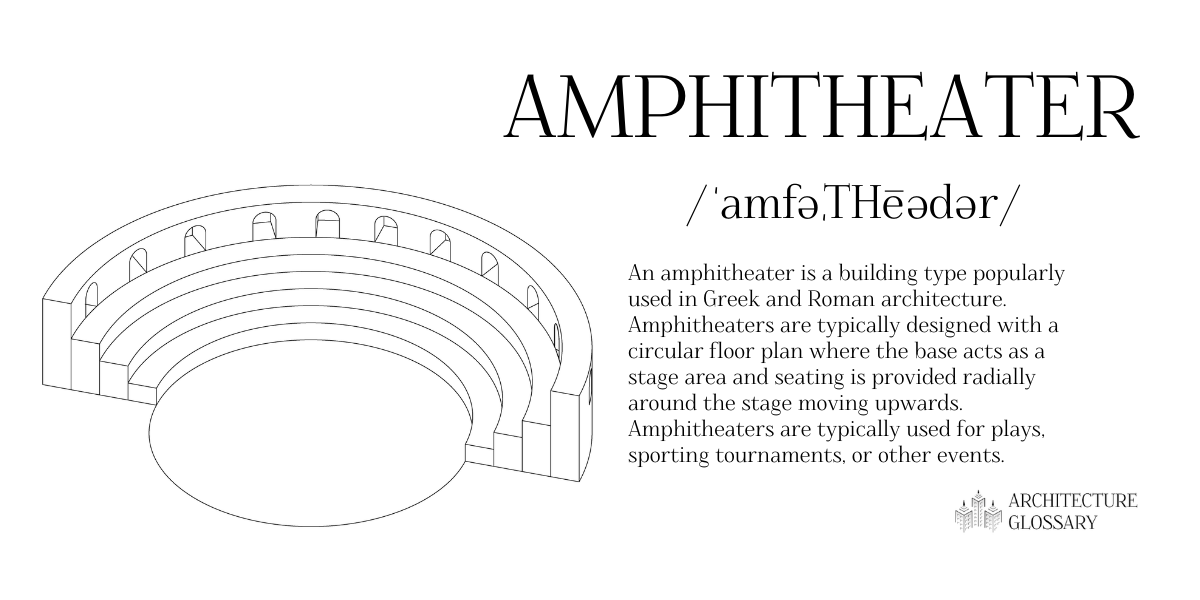
Amphitheatre
An amphitheater is a building jot down popularly used in Greek and Roman architecture.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
Amphitheaters are typically used for plays, sporting tournaments, or other events.
Arcades can happen on the exterior as a semi-enclosed space or on the interior.
Arch
An arch is a form of structure found throughout much of architecture.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
It uses a curve to span a space from two points.
In contemporary building construction, an architrave refers to the molding around rectangular openings like doors and windows.
It features glamorous detailing with often geometric facades and signature vintage fonts.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
Though the style was short-lived, it remains an iconic and recognizable aesthetic.
Designers of Art Nouveau architecture would have a go at create a complete work.
These works were often very cohesive in their design style and intricately detailed.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
Atrium
An atrium is any interior volume in a building.
These spaces are often a major feature and shared space in a building.
Balustrade
A balustrade is a railing or wall on a staircase or balcony.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
It is made from individual posts, called balusters, topped by a rail.
Barrel Vault
A barrel vault is a simple form of a vaultor extruded arch.
Barrel vaults are a continuous extrusion though some vaults featured ornamentation along the surface instead of a plain extrusion.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
A belfry is a common feature in old churches.
Beton brut
Beton brut translates to raw concrete from the original French.
It refers to the aesthetic of unfinished concrete after being removed from formwork.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
This is an important term because the appearance of beton brut was a major pinnacle of modernism.
Biomimicry
Biomimicry is when architecture copies processes or forms found in nature.
Biomimicry is used in architecture both for aesthetics and for buildings functions.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
A buildings system for conditioning air might mimic a forest for efficiency.
Columns may be designed to look like trees simply for aesthetics.
Biophilia
Biophilia is the idea that humans have a natural desire to be surrounded by nature.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
Bracing
Bracing is reinforcement to a structural system.
Brise Soleil
Brise soleil, or brise-soleil, is a French term that translates to sun breaker.
It refers to deflecting the sunlight that heats a building to naturally cool the interior.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
One popular form of deflecting sunlight is through louvers, another term on this list.
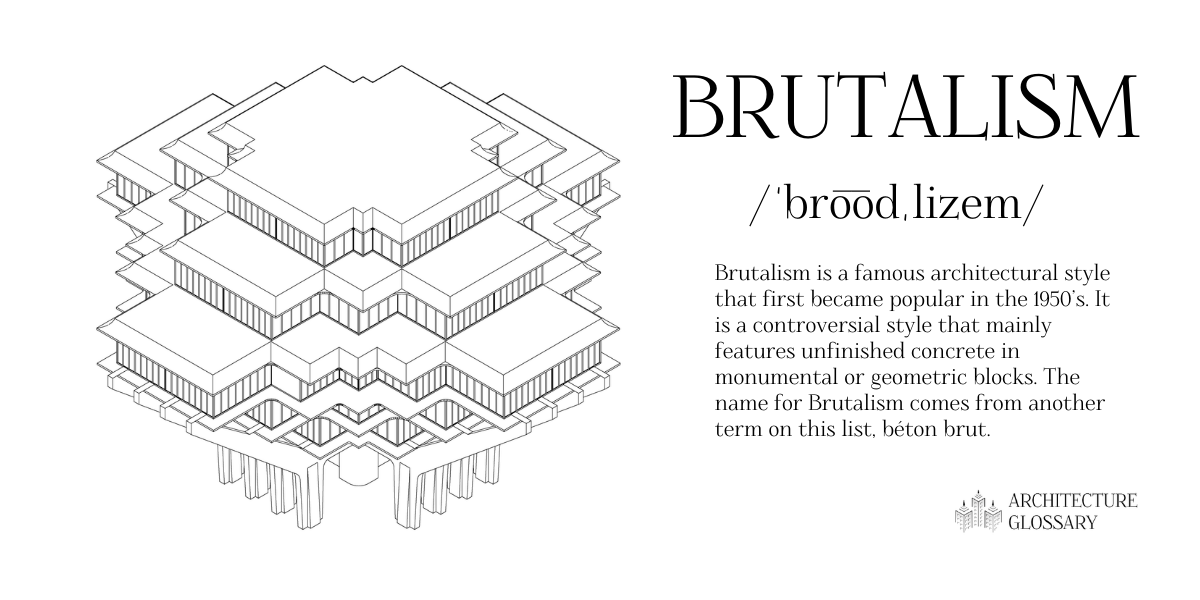
Brutalism
Brutalism is a famous architectural style that first became popular in the 1950s.
It is a controversial style that mainly features unfinished concrete in monumental or geometric blocks.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
The name for Brutalism comes from another term on this list, beton brut.
Buttress
A buttress is a form of structure that helps to reinforce a wall.
Buttresses are built against the wallor near the wall, and they reach across to help support the wall.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
There are a few different kinds of buttresses, including flying buttresses which are defined later in this list.
Byzantine Architecture
Byzantine architecture is a style of architecture that celebrated advancing technology and glamorous detailing.
It became popular under Emperor Justinian in the 6th century.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
Canopies are often built over entrances to shelter people from rain or to provide them with shade.
Cantilever
A cantilever is the portion of a building that protrudes out.
Some cantilevers are simple, like when a deck pushes out just a bit past the last beam.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
The common rule for cantilevers is 1/3 of a section can overhang and 2/3 of a section is supported.
Caryatid
Caryatids are an iconic part of ancient Greek architecture.
A caryatid is a sculptural column in the form of a woman.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
One of the most well-known uses of caryatids is on the porch of the Erechtheion in Athens, Greece.
Circulation also includes the way people move around the outside of a building.
Classical
Classical architecture refers to Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
Colonial Architecture
Colonial architecture can mean a few different design styles.
It happens when a country is colonized and begins to use architecture from the country colonizing it.
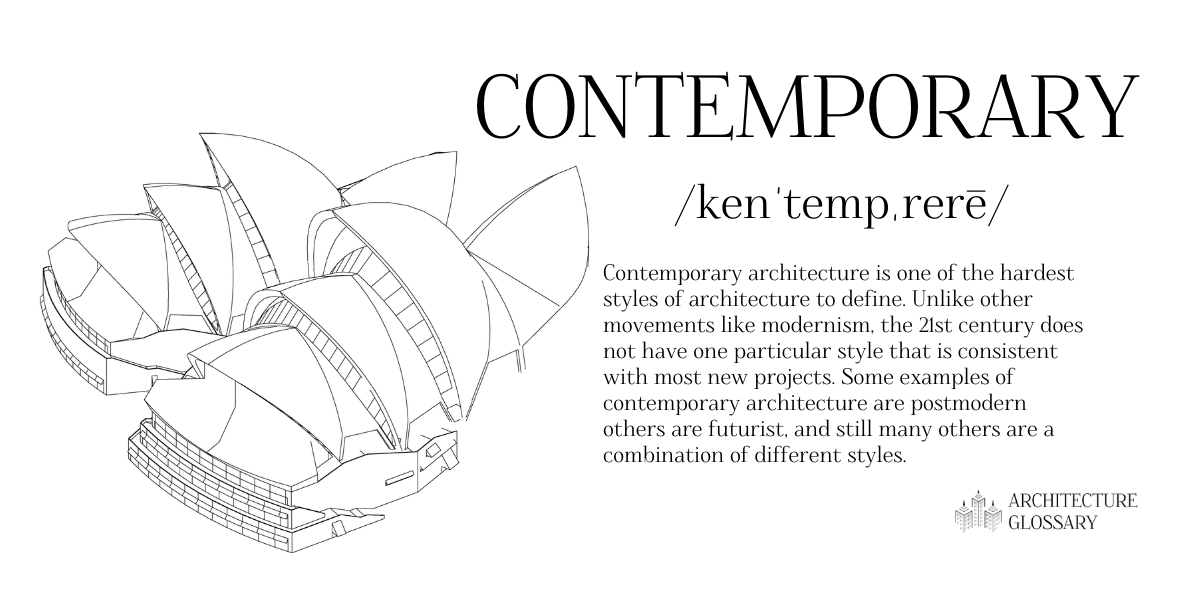
Contemporary
Contemporary architecture is one of the hardest styles of architecture to define.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
Context
In architecture, context refers to the area around an architectural project.
Context plans is a site plan that shows the larger areaor contextsurrounding a project.
Context can also refer to the conceptual related areas instead of a physical place.

Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
For example, someone might talk about a buildings relationship to historical context.
Corbusian
Corbusian is an adjective used to describe architecture of the same style of Le Corbusier.
Acirculation coreis the vertical grouping of an elevator, stair, or pair of the two.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
A core can also refer to aservice corethat is vertically continuous throughout the building.
Corinthian
The Corinthian order is one of three classical orders in Ancient Greek and Roman architecture.
It is the most elaborate of all three orders and was the last developed.
Drawings: Samantha Pires/My Modern Met
The orders are easiest to distinguish by the ornamentation found in the column heads.
Cruciform
Cruciform means taking the form of a cross.
This is a common term in architecture because many buildingsespecially cathedrals and churchesare designed with cruciform floor plans.
Cupola
A cupola is a small dome-like structure that tops a building.
The interior vault of a dome is also called a cupola.
Curvilinear
Curvilinear architecture includes curved lines.
It is often understood as the opposite of rectilinear which is also defined on this list.
Deconstructivism
Deconstructivism is one form ofPostmodern architecture.
It is defined by fragmented and distorted architectural elements.
The most famous example of deconstructivism is by starchitect Frank Gehry.
Though diagrams are used in many fields other than architecture, diagrams are an important part of architecture drawings.
Domes can be made in many sizes and from many materials.
They are major features in countless architectural works.
Doric
The Doric order is one of three classical orders in Ancient Greek and Roman architecture.
It is the simplest of all three orders and was the first to be developed.
The orders are easiest to distinguish by the ornamentation found in the column heads.
In this case, the column head has little ornamentation.
Egress
Building egress is the pathways people take to safely exit a building.
It includes vertical circulation, hallways, and any other movements people take to exit.
Designing the egress of a building is a critical consideration for architects.
Elevation
An elevation is one kind of architectural drawing used to describe a project.
It is a horizontal orthographic projection of a building that represents one facade of a building.
Envelope
In architecture, a building envelope refers to the exterior walls of a building.
Fabrication
Fabrication refers to the way things are put together in architecture.
Facade
In architecture, a facade is a face of the building.
Facades are also sometimes referred to as anelevation, a concept described earlier on this list.
Floor Plan
A floor plan is one of the most critical forms of architectural drawing.
Many floor plans are labeled to best show the functions of each space.
The major load is carried by the outer walls and columns carry the rest.
The open plan allows for more freedom since there are no extra walls to limit design.
The glass on the doors are typically divided into smaller panels.
Frieze
A frieze is a common design element in classic architecture.
Gable
A gable is the triangular portion between intersecting roof pitches.
Gable roofs are efficient because the steep slope allows for water to drain easily and for better interior ventilation.
The area begins to change and the current residents are priced out.
Though it is not a purely architectural term, gentrification affects the urban environment and the buildings built there.
It is called a groin vault because two barrel vaults intersect and create a groin edge.
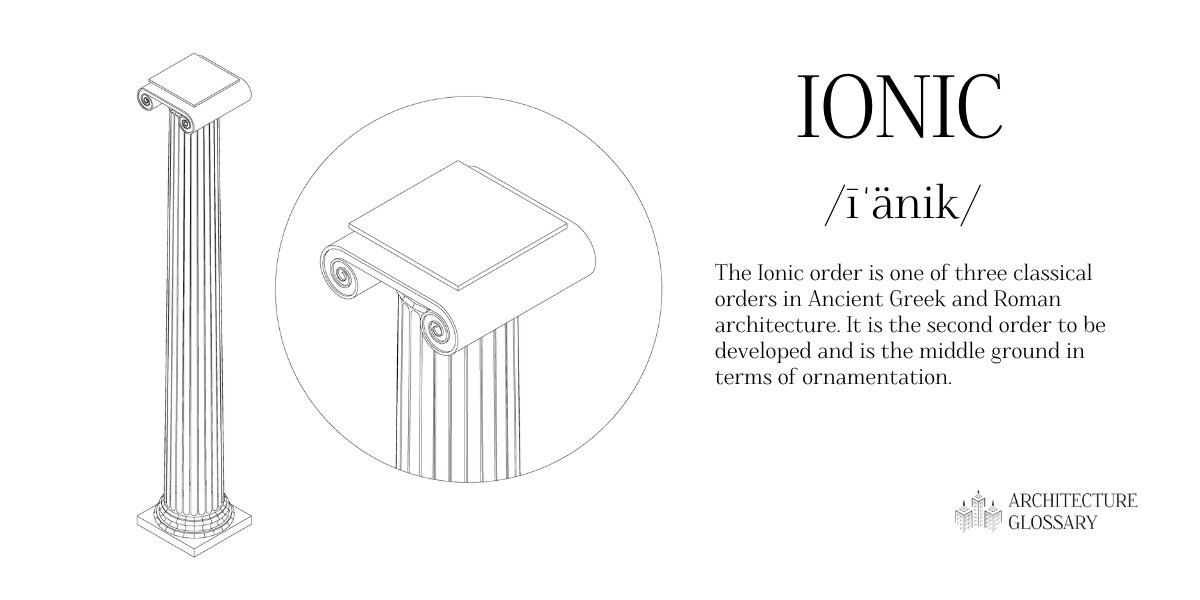
Ionic
The Ionic order is one of three classical orders in Ancient Greek and Roman architecture.
It is the second order to be developed and is the middle ground in terms of ornamentation.
Isometric
Isometrics are a form of architectural drawing that helps represent 3D objects in 2D drawings.
It allows for an easily understandable view of a simple perspective.
In architecture, juxtaposition is when two opposite things are placed next two each other to emphasize the contrast.
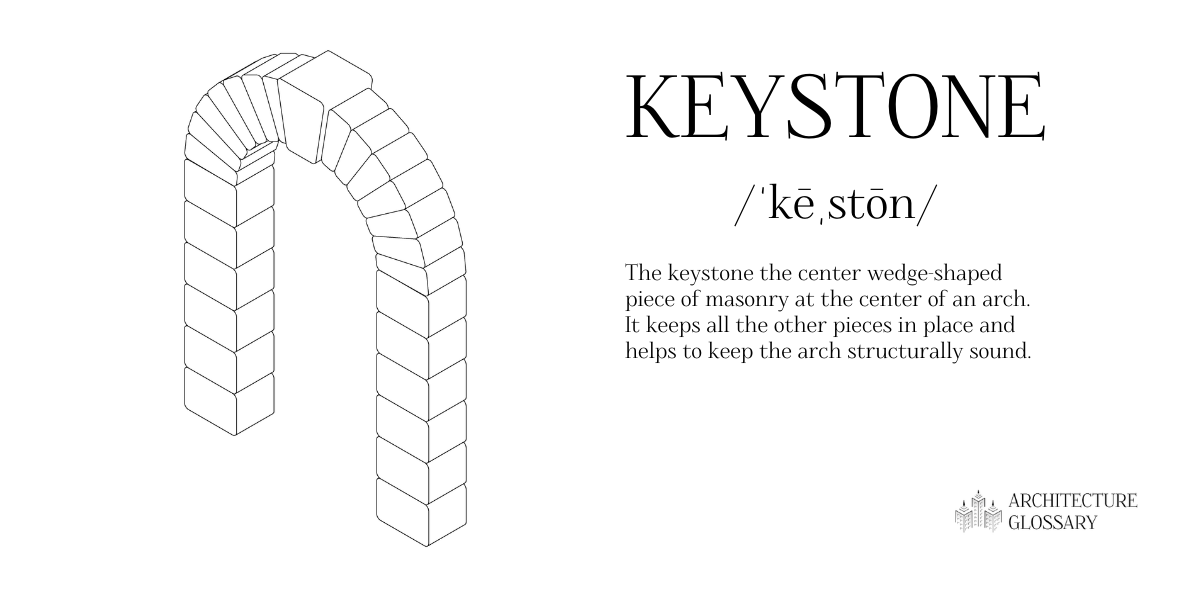
Keystone
The keystone is the center wedge-shaped piece of masonry at the center of an arch.
It keeps all the other pieces in place and helps to keep the arch structurally sound.
Lintel
A lintel is a horizontal block that spans an opening.
It is often found over doors or windows.
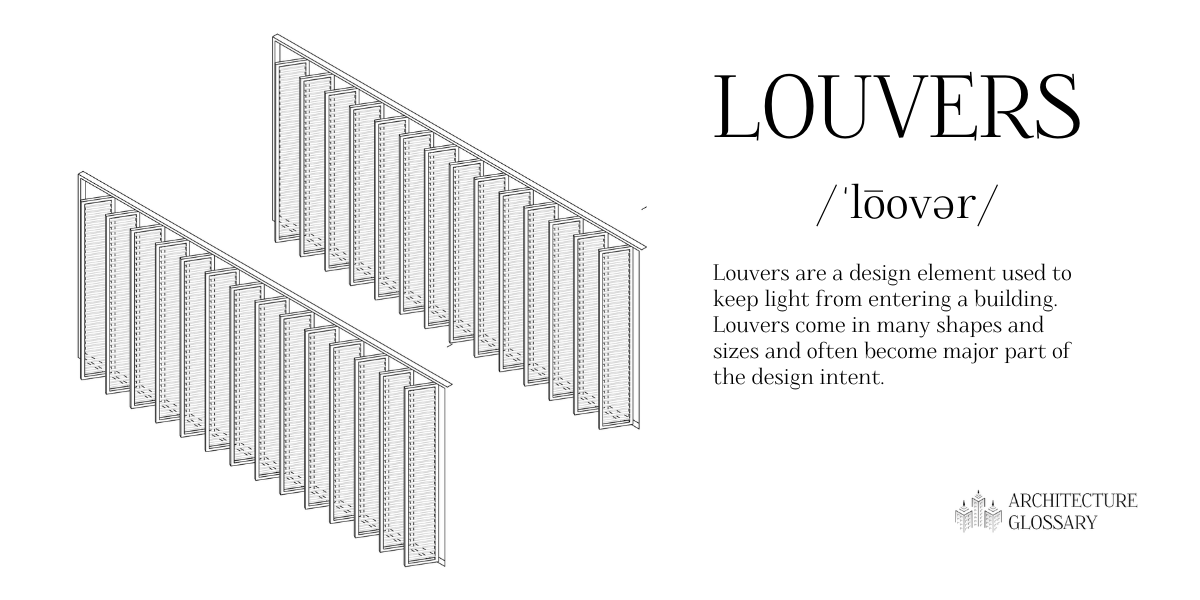
Louvers
Louvers are a design element used to keep light from entering a building.
Louvers come in many shapes and sizes and often become a major part of the design intent.
Maqsurah
A maqsurah is a common mosque element.
It is a small enclosed area near themihraba term also defined on this list.
Massing
A massing is the general size and shape of a building.
Massings are often the first step in a conceptual study when designers define the general boundaries of the building.
The term massing is used later in the design process to describe architectural volumes.
Mezzanine
A mezzanine is a half floor in a building.
Mezzanines are generally open to an atrium that is typically a double-height space or taller.
Mihrab
A mihrab is an important design element in a mosque that serves a critical function.
It is a wall niche that helps orient the congregation towards Mecca during prayer.
Minaret
A minaret is a traditional tower in or near a mosque.
It is an iconic design element of the mosque typology but it also serves multiple functions.
Minarets are used to call Muslims to come and pray at the time of prayer.
Modern Architecture
Modern architecture does not just mean the architecture of today.
These units can be stacked in interesting ways.
Monumental
Architecture that is monumental has an air of permanence or heaviness.
Famous architect Louis Kahn described monumental architecture as inspiring a spiritual quality.
Mullions support the structure of the window and allow for smaller portions of glass.
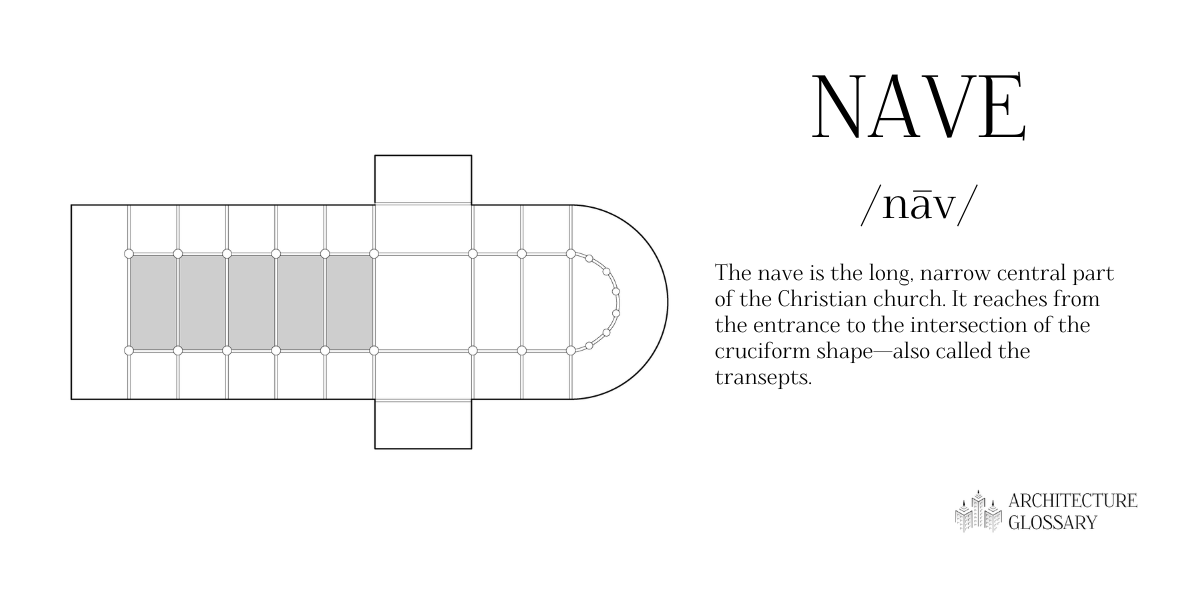
Nave
The nave is the long, narrow central part of the Christian church.
It reaches from the entrance to the intersection of the cruciform shapealso called thetransepts.
Oculus
An oculus is a circular opening at the center of a dome.
One of the most popular examples of an oculus is in the Pantheon.
Ornamentation is often embedded in structures, windows, or other pieces of architecture.
In some styles, it is difficult to distinguish what is ornamentation and what is pure function.
Palazzo
The palazzo is an architectural throw in in the 19th and 20th centuries.
They are large monumental buildings inspired by the palaces of wealthy Italian Renaissance families.
Parti
The word parti comes from parti pris which means decision taken.
A parti is a concept or scheme that describes the concept behind an architectural project.
A parti typically takes the form of adiagram.
Pavilion
In architecture, a pavilion is an informal structure that is often temporary.
They are sometimes architectural installations or additions to gardens or public areas.
Often found in ancient Greek and Roman temples, pediments were typically filled with relief sculptures.
It considered architecture in combination with landscape for one composed scene.
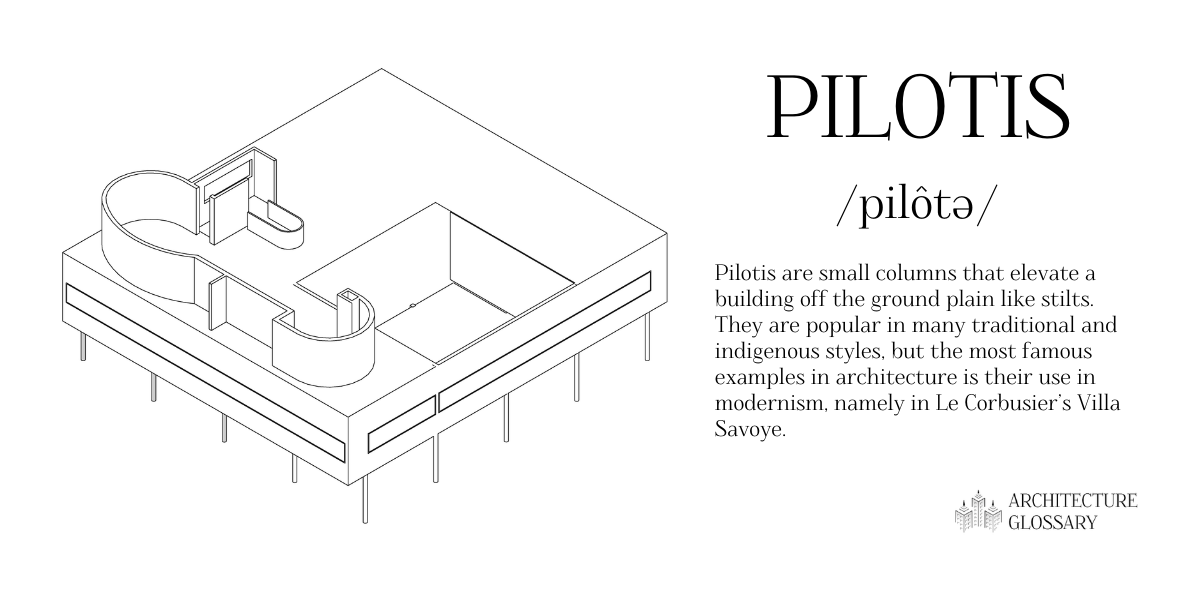
Pilotis
Pilotis are small columns that elevate a building off the ground plain like stilts.
Portico
A portico is a porch at the entrance of aClassicalbuilding.
The portico is covered by a roof that is held up by columns.
It is a form of acanopy, another term defined on this list.
The style was playful and quirky because it believed that modernists were too boring and focused on function.
It was characterized by fun colors and interesting geometries.
It is often a path that was carefully considered as a series of framed perspectives.
Program
In architecture, building program refers to the function of a space.
A cultural center may include building programs like classrooms, event spaces, and a cafeteria.
Rectilinear
Rectilinear designs are made up of mostly straight lines and right angles.
It is often understood as the opposite of curvilinear which is also defined on this list.
Renaissance
Renaissance architecture was the design style of a period of European revival.
Much of the style was inspired byClassicalarchitecture.
The characteristics of Renaissance architecture focused on proportions in the search for perfect beauty.
Rib vaults are extremely popular structural ideas found throughout many styles.
Romanesque
Romanesque architecture is a historic style popular for a range of time in medieval Europe.
Screen
In architecture, a screen is a facade element that is often partially transparent or porous.
Setback
In architecture, a setback is when a building is recessed back.
A setback could also refer to when a portion of a building is setback from the level below it.
Many NYC towers include setbacks as they grow taller.
Solar Gain
Solar gain is the amount of sunlight that enters a building or hits a material.
Minimizing solar gain is often necessary to improve the cooling of a building.
Spire
A spire is the ornamental tip of a tower.
Stoop
In architecture, a stoop is a porch with steps at the entrance of a building.
Stoops are a great example of architecture playing an important cultural role.
Tracery
Tracery is the functional ornamentation that breaks up a larger window into smaller panels.
Turret
A turret is a small tower typically at the corner of a building.
They are also sometimes used in homes and other building types purely for aesthetics.
Typology
Typology is the way to classify things according to similar characteristics.
Vault
A vault is a self-supported arched extrusion.
There are many forms of vaults that are defined by how the arch is continued.
On this list, we definebarrel vault,groin vault, andrib vault.
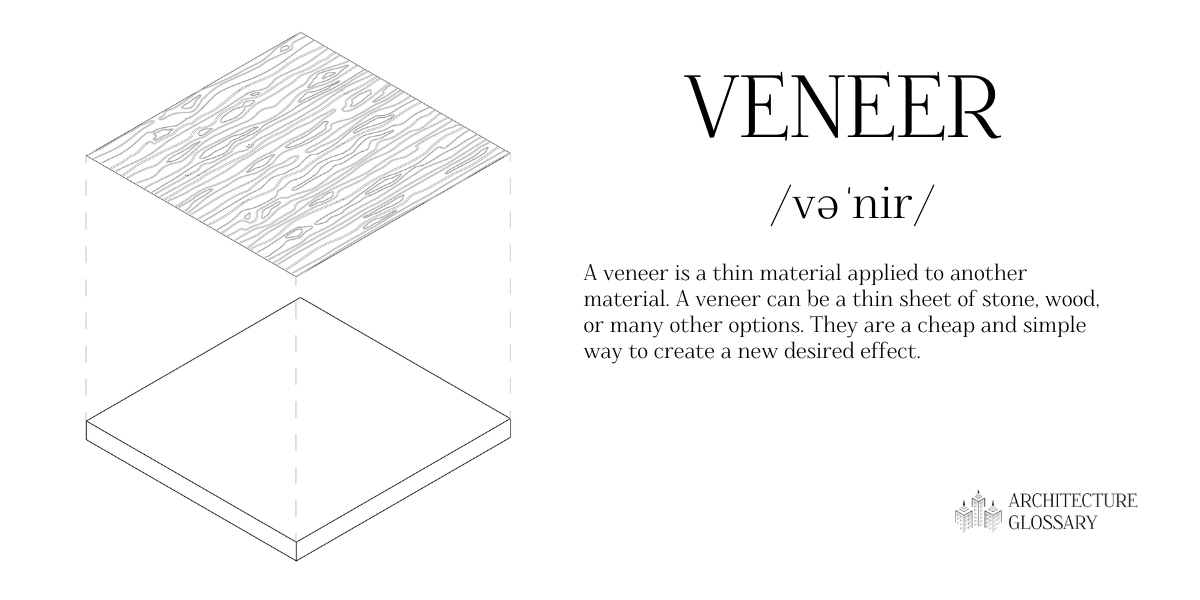
Veneer
A veneer is a thin material applied to another material.
A veneer can be a thin sheet of stone, wood, or many other options.
They are a cheap and simple way to create a new desired effect.
Vernacular
Vernacular architecture is any style that is native to a specific area and time.
Vernacular architecture is based on tradition and often relies on materials and knowledge from the area.
Vestibule
A vestibule is a small entrance area that people pass through before reaching a larger space.
This process saves money in the conditioning of a space and is also more environmentally friendly.
Victorian Architecture
Victorian architecture is a style popular during the end of the 19th century.
Victorian architecture is characterized by pitched roofs, colorful brick, ornate gables, and the tall, iconicturrets.
It is used as a presentation tool during the design and construction of an architectural work.
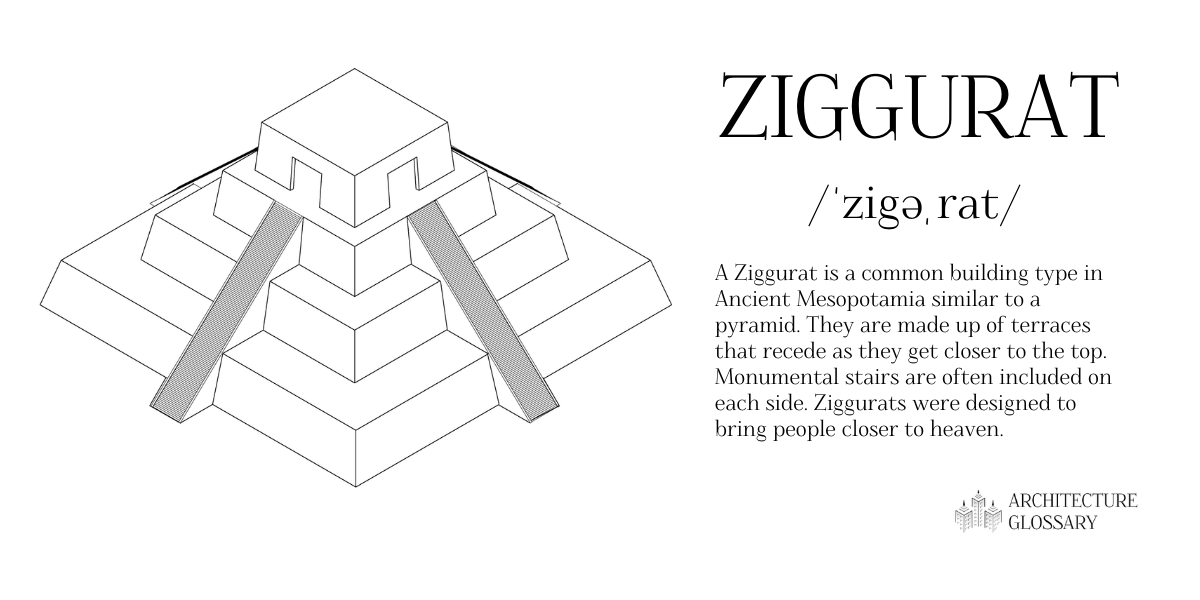
Ziggurats are made up of terraces that recede as they get closer to the top.
Monumental stairs are often included on each side.
Ziggurats were designed to bring people closer to heaven.