A famous example is theNazca Linesin Peru.
These etchings ofanimals, humans, and abstract pictures date back to between 500 BCE and 500 CE.
The tool scans massive amounts of aerial footage, in this case from the Nazca Desert in Peru.
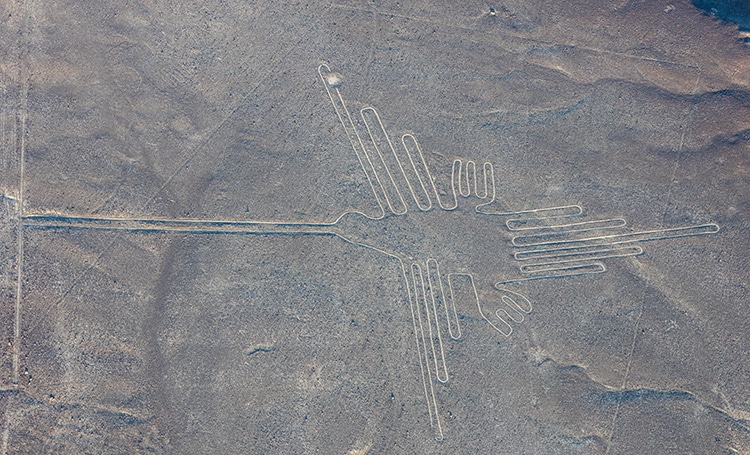

Hummingbird lines. (Photo: Diego Delso, delso.photo viaWikimedia Commons,CC BY-SA 4.0)
The team claims the deep learning tool is 21 times faster than searching with human eyes.
Since known glyphs are similar, these similarities help identify the new.
Rather than looking for the same etched cat as seen elsewhere, the tool looks for component parts.
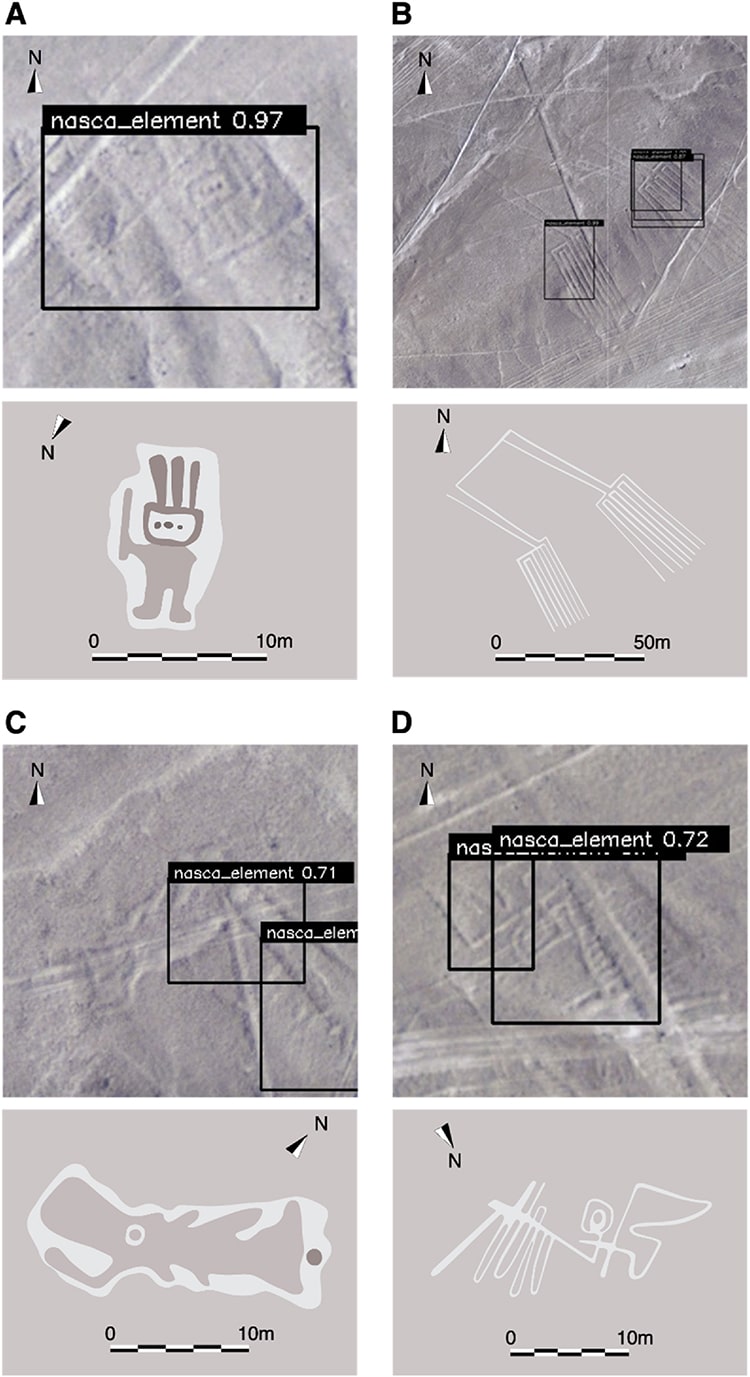
The newly discovered geogylphs. (Photo:M Sakai, et al.)
By doing this, new designs can be picked out.
Based on such learning, they acquire the ability to accurately detect objects that appear in new images.
It demonstrates high performance in tasks such as image recognition, speech processing, and natural language processing.
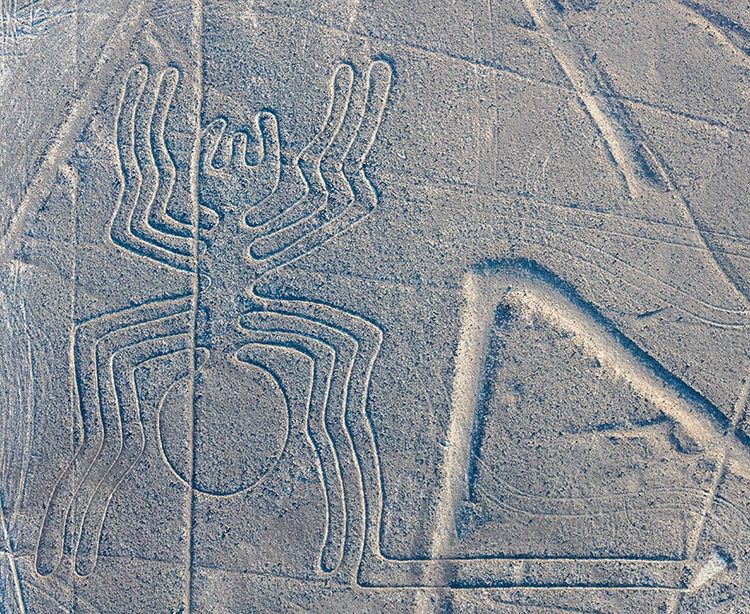

Spider. (Photo: Diego Delso, delso.photo viaWikimedia Commons,CC BY-SA 4.0)
These include trees, flowers, cats, lizards, and monkeys.
The newly discovered geogylphs.
(Photo:M Sakai, et al.)
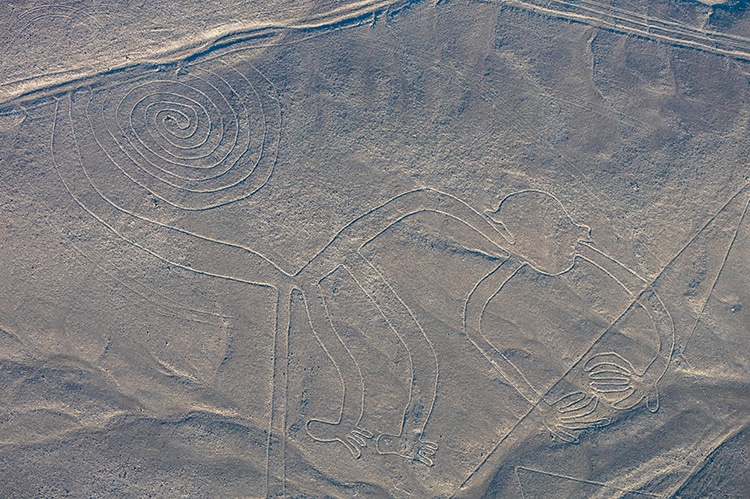

Monkey. (Photo: Diego Delso, delso.photo viaWikimedia Commons,CC BY-SA 4.0)
(Photo: Diego Delso, delso.photo viaWikimedia Commons,CC BY-SA 4.0)
Monkey.