NGC 5468, a galaxy containing Cepheid variable stars.
If so, perhaps no true unexplainable problem existed.
However, a study recently published inThe Astrophysical Journal Letterslays this debate to rest.
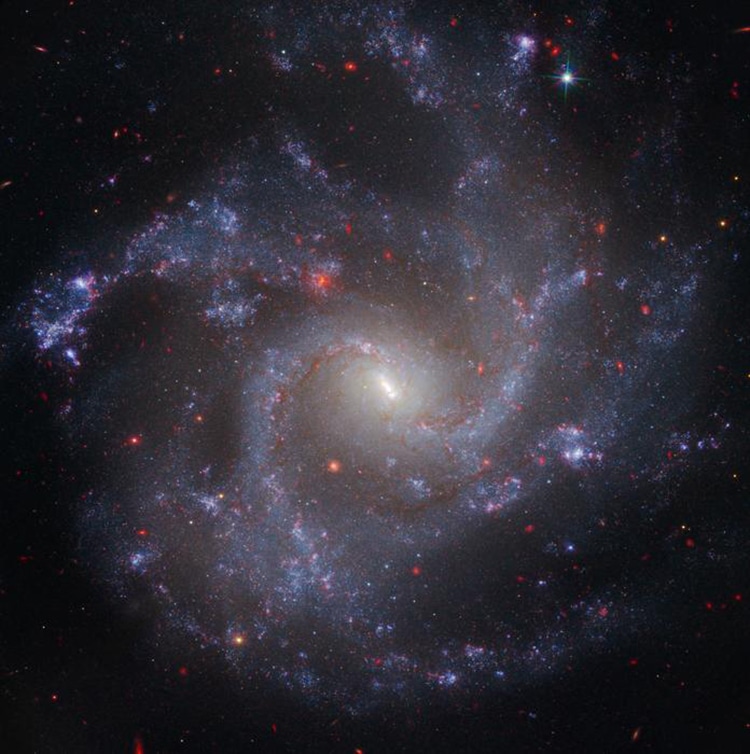

NGC 5468, a galaxy containing Cepheid variable stars. (Photo:NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Adam G. Riess (JHU, STScI))
The rate of the expansion of the universe is known as theHubble constant.
TheLambda CDMthe current governing system of measuring universe expansion by examining the cosmic microwave backgroundbreaks down at these points.
These are dying, pulsating stars whose light’s red-shift can expose the past of the universe.
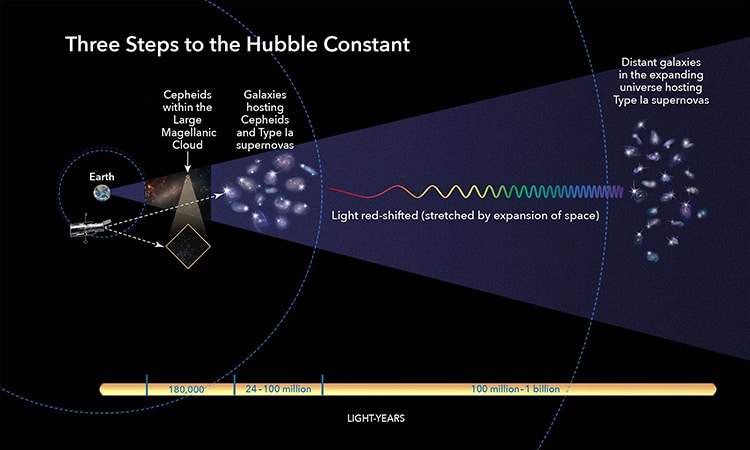
Showing how the Hubble constant is calculated. (Photo:NASA, ESA, and A. Feild (STScI))
Combining Webb and Hubble gives us the best of both worlds.
Exactly how fast is it expanding?
Showing how the Hubble constant is calculated.