Towards the end of the 18th century, a new art movement emerged calledRomanticism.
At the forefront of this remarkable style was the French artistEugene Delacroix.
Here, we will learn more about Delacroix’s art and the characteristics of his style.

Who was Eugene Delacroix?
His oeuvre spanned contemporary events, mythological scenes, Orientalism, and portraiture.
As an avid student ofcolor theory, he created thoughtful palettes which enhanced the subject matter of his paintings.

Eugène Delacroix, “Self-Portrait,” 1837 (Photo:Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain)
Expressive Brushstrokes
Delacroix’s approach to painting is often seen as a precursor to the Impressionists.
He did not venture to disguise the texture of hisbrushstrokesand instead made them more aggressively visible.
These traits helped him express mood and create a sense of movement.
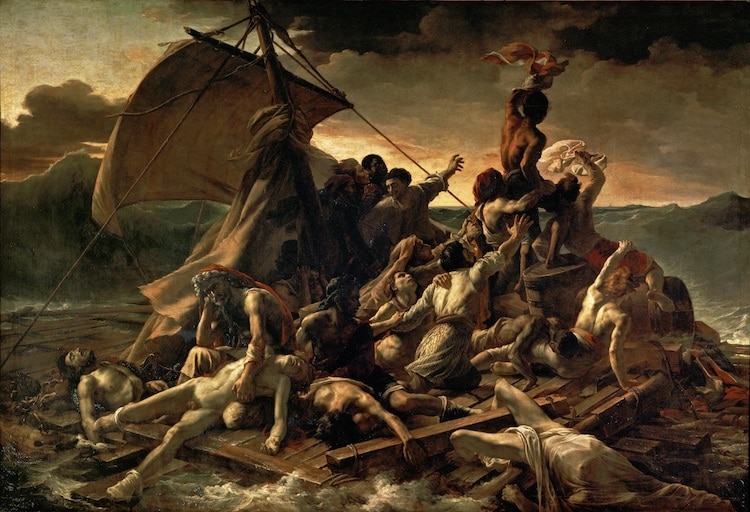

Théodore Géricault, “The Raft of Medusa,” 1819 (Photo:Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain)
As a result, he became known for constructingdynamic compositionsthat utilized foreshortening, perspective, and twisting figures.
Additionally, the wild nature of animals embodied the ideals of Romanticism.
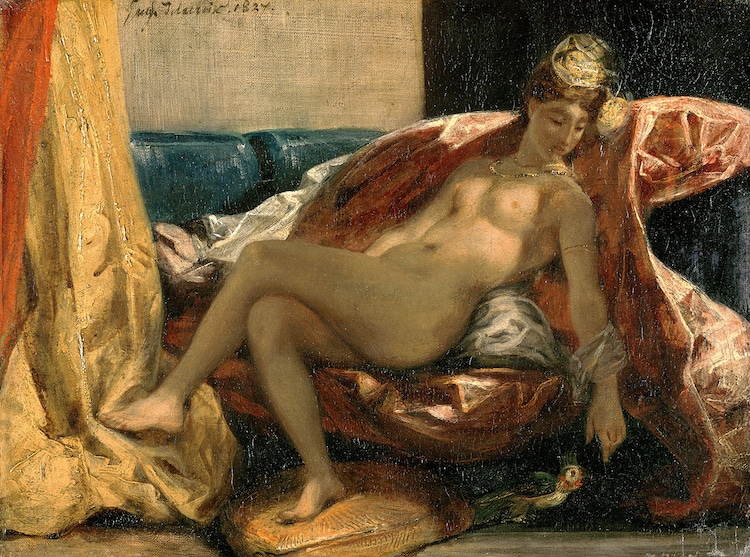
Eugène Delacroix, “Woman With a Parrot,” 1827 (Photo:Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain)
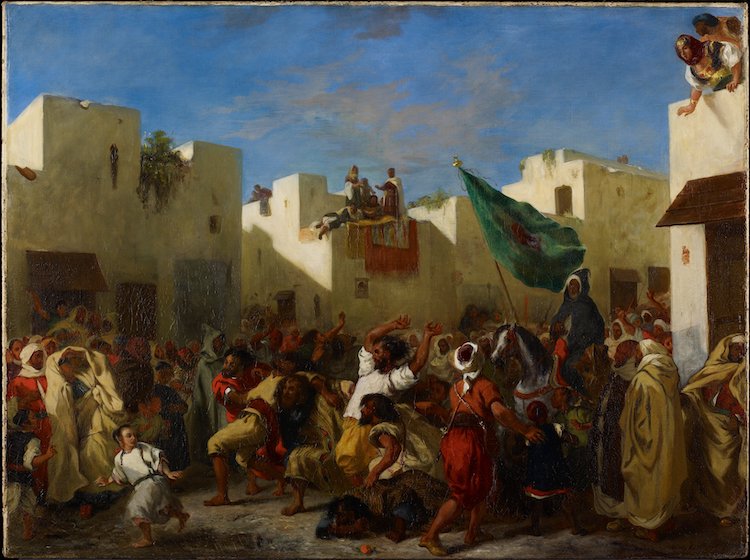

Eugène Delacroix, “The Fanatics of Tangier,” 1837-8 (Photo:Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain)
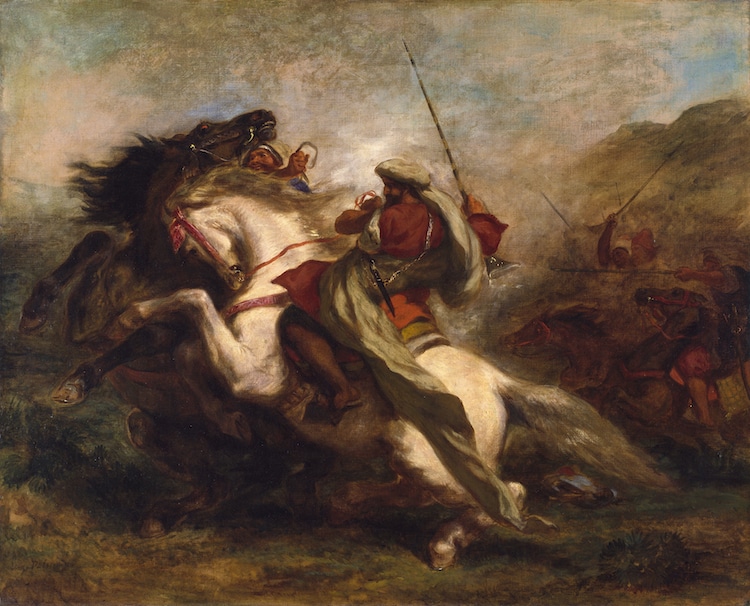

Eugène Delacroix, “Collision of Moorish Horsemen,” 1843-44 (Photo:Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain)
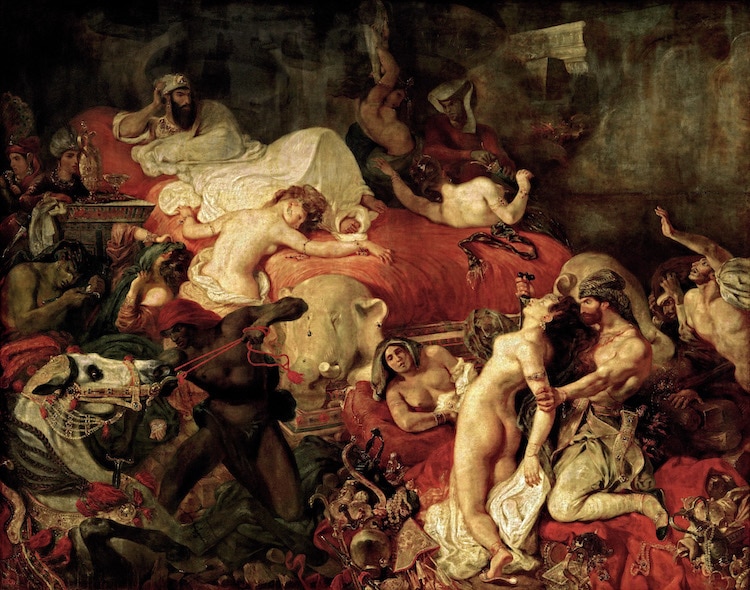

Eugène Delacroix, “Death of Sardanapalus,” 1827 (Photo:Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain)
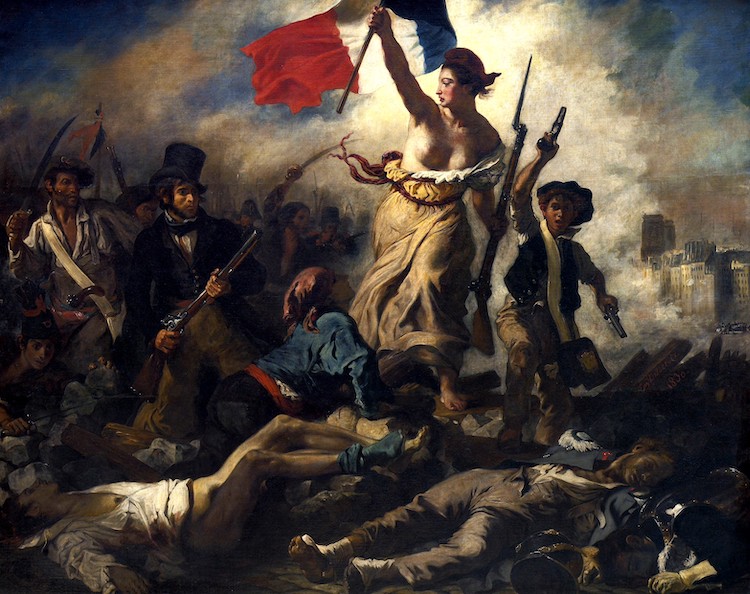

Eugène Delacroix, “Liberty Leading the People,” 1830 (Photo:Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain)
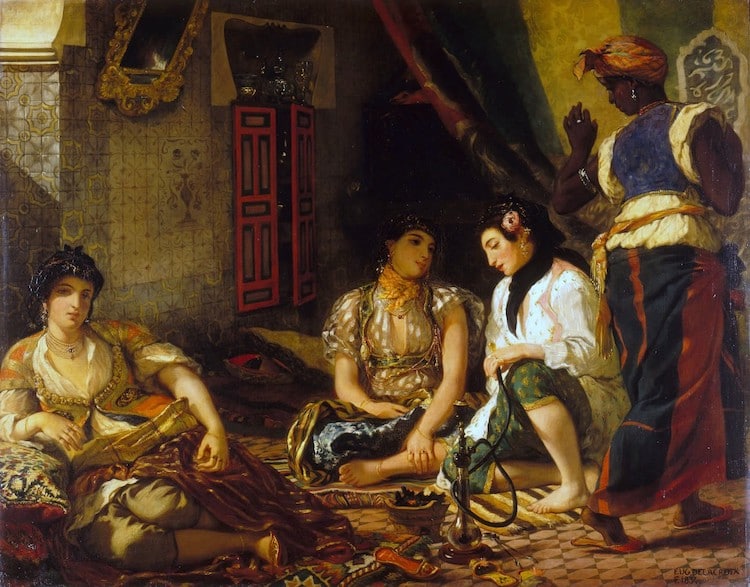

Eugène Delacroix, “The Women of Algiers,” 1834 (Photo:Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain)
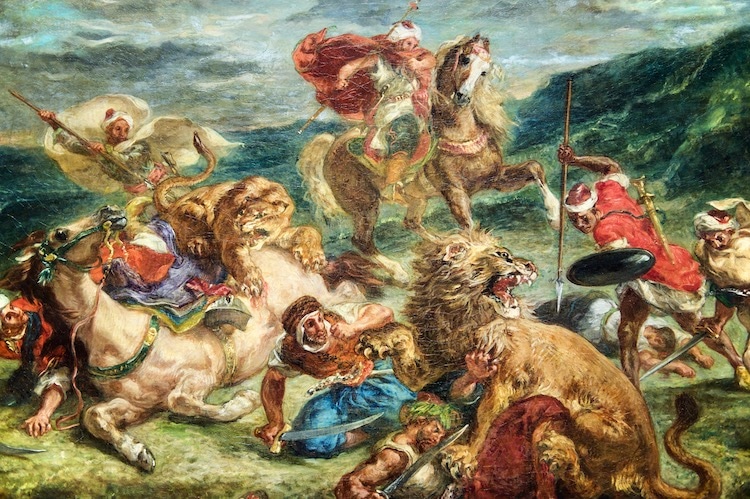

Eugène Delacroix, “Lion Hunt,” 1860-1 (Photo:Wikimedia Commons,CC BY-SA 4.0)